The ability to see the world through the eyes is indeed a thing everyone should be grateful for. You should always take care of your health so that you can have a fulfilling life and be able to enjoy the beauty of the world through the gift of eye vision. However, there are many eye disorders that could cause a person to have difficulty to have a normal eyesight and in some instances, it may even cost their life when left untreated. In this article, we will be learning about one of the many eye disorders known as papilledema.
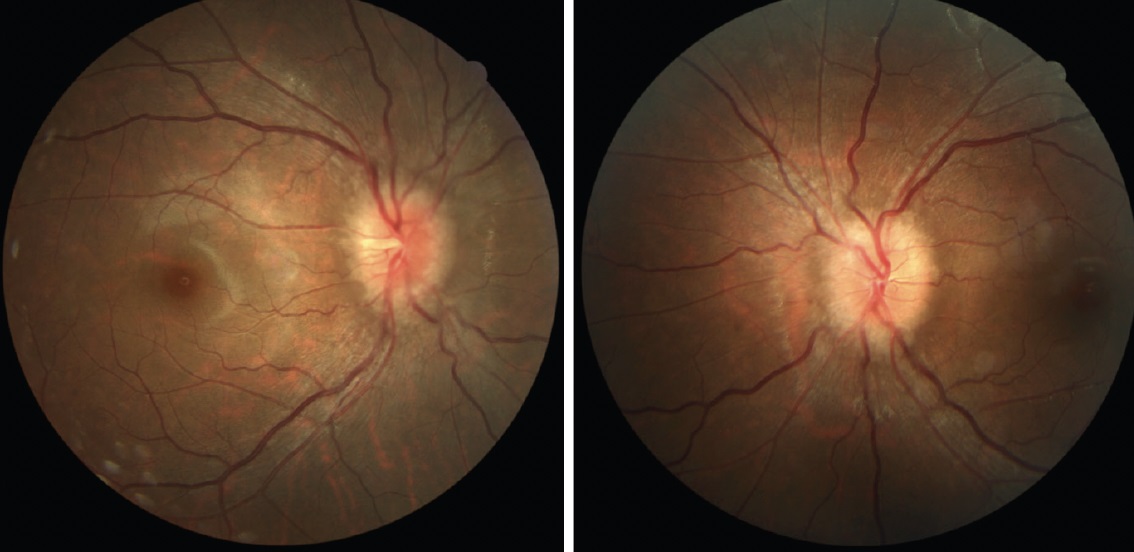
Papilledema is the swelling of the optic disc. Optic disc contains the optic nerve that connects the eyes and brain. The swelling is caused by the raised intracranial pressure (ICP). ICP is usually the buildup of pressure around the brain and can be caused by many reasons. In most cases of papilledema, it is often a sign of an underlying serious medical condition that needs immediate attention such as haemorrhage and brain tumour but at times doctors could not find the source of the problems.
The brain is surrounded by many nerves, blood vessels and fluids while located in the skull. There are many reasons behind a papilledema. Anything that causes an increase in ICP may contribute to the swelling of the optic nerve. Increased ICP can be caused by the brain volume become too large for the skull such as brain tumour, brain haemorrhage and brain swelling (edema), size of the skull too small for the brain such as in craniosynostosis, an obstruction to the cerebrospinal fluid flow (CSF) such as colloid cyst, increased productions of CSF in choroid plexus papilloma and reduced absorption of CSF such as in meningitis. CSF is a fluid surrounding the brain.
Development of papilledema may be weeks if there is only slow and mild rise in ICP but severe and rapid changes in pressure can cause papilledema to develop within a few hours to a day. When there are no reasons behind the rise in ICP, this is known as idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Papilledema may also be caused by side effects of medications. Beside the cause of papilledema, risk factors do play a role for a person to develop papilledema. Risk factors are things that a person has that if a person has any of the risk, they have high chances for the disease, in this case papilledema. Risk factors include recent weight gain of additional 5 to 15{47beef4fa453f14f0944959b9bf73fa5db70c22fad4a70ee729750c6b8a1f449} of the initial body weights and underlying medical conditions such as polycystic ovarian syndrome, anaemia, thyroid disease, obstructive and sleep apnoea.
The symptoms may not be obvious during the early stage of papilloma. Doctors may accidentally discover it during a routine eye exam. As time goes by, patients will start to have vision problems, typically in both sides of the eyes. It is common for visual changes from blurry vision to grey or black in less than 30 seconds. Patients often describe their vision as if a veil has fallen over the eyes. The blackouts are often triggered by change in position such as from standing up suddenly or triggered by increased pressure in the abdomen such as coughing or straining when bowel movement. At times, patients may experience flashing lights in the shape of arcs. Other visual changes do occur over time such as smaller vision fields with larger blind spots. Other symptoms include headache and vomiting.
It is important to treat papilledema as to leave it untreated will lead to blindness. Doctors are able to diagnose this condition by using ophthalmoscope and visual field test. To find the cause of the papilledema, further tests such as imaging tests like CT-scan or MRI will be done especially when doctors suspect there is damage to the brain as this can be life-threatening. If brain scans do not show obvious abnormality, patients will need to go for lumbar puncture procedures to evaluate CSF.
The swelling of the optic disk will gradually go away over 6 to 8 weeks once the cause of the papilledema is treated or the spinal fluid has returned to normal. In case of idiopathic intracranial hypertension, it may take longer treatment and longer time for symptoms to disappear. Brain surgery might be recommended if medications and spinal tap do not work to relieve pressure.
In essence, papilledema can lead to permanent vision loss if it is not identified and treated well. The main symptoms of papilledema are the changes of vision from blurry to black or grey. Treatment of papilledema depends on the cause of the disease. It is important to talk to a doctor if you often have headache, nausea and vomiting that is not known why. This is more important and urgent if you have fever, high blood pressure or sudden weight gain. Mild papilledema may last for months to years without significant lose of vision but once a person starts to lose vision, it can become permanent within days or weeks if it is not treated early.
Buy Keppra 500mg Tablet 10s (strip).