What are germs?
The theories of single-cell organisms, fungi, and numerous other living, growing organisms have been discussed in science class. These organisms are referred to as “germs” or, in some cases, “microorganisms” generally. Microorganisms are divided into four categories: bacteria; viruses; fungi; and protozoa (protozoa). “Germs” is a catch-all term that refers to bacteria, viruses, and other microscopic particles that cause illness in humans and are not specifically classified.
Oh My Gut!
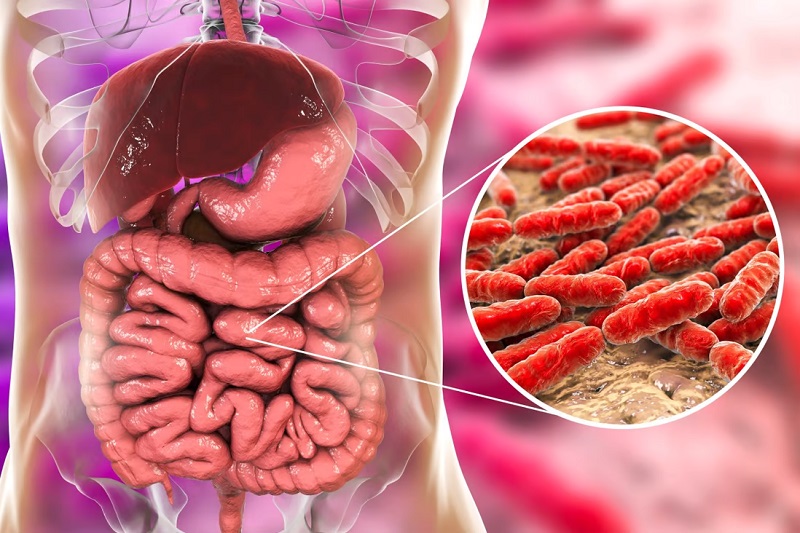
Did you know that, according to scientific literature, the number of bacteria living in and on each of us is estimated to be 100 trillion? Yes, there are numerous germs in the human intestines. The human microbiota is a collection of microbes and it contains ten times the number of cells found in the human body as the human body itself. There are a lot of different kinds of microbes in our bodies. Let’s take a closer look at them.
Bacteria are unicellular microorganisms that make up roughly 90{d758bea15a7466bf6aaf2e75080f34ed49ceb83a76468a28ea6d69025fc70106} of the population in our gut. The term “gut microbiota” refers to the collection of microorganisms that typically live in the gut. This is because we have lifelong relationships with our gut microbes. We refer to them collectively as the gut microbiome.
Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Verrucomicrobia are the five major phyla of bacteria found in our digestive tract. Escherichia coli and Salmonella are two examples of Proteobacteria strains. Some of them are harmful to humans, but most are not.The microflora in the intestines plays a big role in health and disease. However, this ecosystem is still very poorly understood and defined. On the other hand, the presence of intestinal germs helps to protect epithelial cells from damage, regulates the fat storage of the body and encourages the new formation of blood supply for the intestines.
When do we develop these germs in our gut?
According to the research, in our mother’s womb, we live in a bacteria-free environment, which is well protected by our mother’s body and immune system. However, during delivery, we are exposed to bacteria as soon as the amniotic sac ruptures. Through the mother’s vaginal canal, we are exposed to microbes.While if a baby is born via caesarean section, it receives the first exposure from the caregivers’ skin. We are quickly exposed to a variety of bacteria once we enter the world fully.We got it from the skin and breastmilk, as well as microbes in the delivery environment, such as the hospital. These are known as “pioneering immigrants”.
As the baby grows, a stable gut microflora composition is achieved. This happens at the same time as the child moves to a more adult-like diet and the immune system grows stronger. The gut microbiota changes throughout life as a result of changes in age, disease states, diet, and geographic location, as well as the consumption of drugs and food supplements, including antibiotics. Thus, each of us has our own unique gut microbiota.
When does your gut become unbalanced?
The intestinal gut flora may be altered or disturbed, usually due to the widespread use of antibiotics. Besides that, dietary changes (especially the trend toward more highly processed fast foods) and more hygienic living conditions have resulted in the loss of some potentially beneficial microbes in the gut. Whatever the underlying reason, there is really no doubt that our relationship with microbes has begun to shift, with far-reaching consequences.Let’s take a few of them into account.
1.Anxiety and depression
Researchers have discovered a link between the brain and the gut. The digestive tract, like the brain, is full of nerves known as the enteric nervous system, or ENS, also known as the “second brain.” The central nervous system has neurons and neurotransmitters that are very similar to those in the enteric nervous system. When there is a change in the intestinal flora, it disturbs the production of neurochemicals that are required by the brain.
2.Immune system problems
The human immune system is a complex mechanism.A strong immune system is needed to get rid of powerful cancerous mutant cells and fight infections. An overactive or uncontrolled immune system is very likely to cause enormous damage to the human body. The prevalence of autoimmune disorders has increased, and it has been linked to changes in gut microbes. According to some studies, the widespread use of antibiotics, unhealthy food habits, and the elimination of chronic parasite infections may have resulted in a microbiota that is incapable of establishing a balanced immune response, which may account for the rise in autoimmune problems.
3.Inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a catch-all term for disorders characterized by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are two types of IBD. Diarrhea, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, fatigue, and weight loss are common symptoms of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.There is no known cause for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), but the most ubiquitous hypothesis suggests that it is caused by an exaggerated immune response triggered by environmental factors against an altered gut microbiota or pathogenic microorganisms in a genetically predisposed host.
Ultimately, a healthy gut refers to a stronger immune system, improved mood, pain-free digestion, as well as a healthy brain and heart. It is critical to naturally maintain a healthy and balanced gut environment. Following these tips will help you improve or maintain your gut health.
- Consume Foods High in Fiber
- Exercise Frequently
- Reduce Your Levels of Stress
- Take probiotics supplements
- Incorporate yogurt into their diet
- Ensure adequate sleep
Lastly,the presence of good bacteria and bad bacteria work homeostatically in harmony to provide the maintenance of the digestive system, thereby providing energy and boosting the function of the immune system.Thus,savour each moment of your life, as you only have one.
Do not hesitate to consult a doctor through Ask a Doctor for your health concern.